Aggregations
Aggregations are a way to summarize data over a time window. They are used to calculate the feature value, and are defined in the Builder of the feature.
Since aggregations are quite complex to achieve in a production system, Raptor allow you to define them in a declarative way, and then it will take care of the implementation.
Aggregation Types
Raptor supports the following aggregation types:
- Count - Counts the number of values in the time window.
- Sum - Sums the values in the time window.
- Average - Calculates the average of the values in the time window.
- Min - Calculates the minimum value in the time window.
- Max - Calculates the maximum value in the time window.
How does it work?
Raptor implements aggregations differently in production, and in development/training mode:
- In development mode, Raptor will use native Pandas to aggregate the data over the whole dataset.
- In production mode, since we don't have the whole dataset yet, Raptor uses the "bucketing algorithm" to aggregate the data over the time window.
How does it work in production?
In production, we are required to achieve a quick latency, scalability and cost-effectiveness. Considering these requirements, we cannot recalculate the aggregation on every request and go through all of our data points.
To achieve that, we are using a "bucketing algorithm" that will split the calculation over a smaller granularity( buckets), and then aggregate the results.
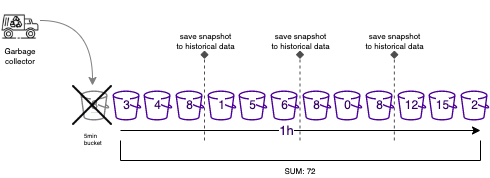
In the example above, we are calculating the Sum of the values over the last 1 hour, with a 5 minutes granularity. That means that we will get the sum of the values over the last hour with an accuracy of 5 minutes.
To achieve that, we will split the time window into 12 buckets, each bucket will include the sum of the values over a period of 5 minutes, then we will summarize the results of the buckets to get the final result.